Received: November 2021
DOI 10.17677/fn20714807.2022.03.02
Fluorine Notes, 2022, 142, 3-4
MECHANISM FOR INITIATION CATION POLYMERIZATION OF p-METHYLSTYRENE IN THE PRESENCE OF BF3 ∙ HF CATALYST IN TOLUENE AT 1:4 RATIO
V.A. Babkin1, A.V. Ignatov2,3, E.S. Titova2, 3, A.I. Rakhimov2
1Volgograd State Technical University (Sebryakovsky br.), 403343 Volgograd Region, Mikhailovka, Michurina st., 21.
e-mail: babkin_v.a@mail.ru
2Volgograd State Technical University, 400005 Volgograd, Lenin av., 28.
e-mail: organic@vstu.ru
3Volgograd State Medical University, 400131 Pavshikh Bortsov sq., 1.
e-mail: titova051@rambler.ru
Abstract: In this paper, initiation mechanism of cationic polymerization of p-methylstyrene in the presence of a complex catalyst BF3 ∙ HF at the ratio of 1:4 has been studied by ab initio method. The values of activation energies and reaction enthalpy are estimated.
Keywords: initiation mechanism, p-methylstyrene, boron fluoride catalyst – hydrogen fluoride, toluene, activation energy, enthalpy, ab initio method.
Introduction
Boron fluoride - hydrogen fluoride (BF3∙HF) is a typical catalyst for cationic polymerization [1], the classical stages of which are initiation, growth and termination of material chain [2]. It is obvious that variation in nature of Lewis acid (for example, BF3, BF2CH3, BF(CH3)2, B(CH3)3, BF2CH5, etc.) and Brønsted acid (HF, HCl, HBr, etc.) in catalyst composition, as well as the stoichiometric composition “catalyst : solvent” 1:1 (in this case - toluene), 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, etc.) opens up the possibility of controlling the polymerization process at initiation stage in practice up to obtaining a polymer (oligomer, telomer, and, in particular, poly-p-methylstyrene) with specified physico-chemical properties.
Until now, a number of important fundamental issues concerning the mechanisms of elementary acts of cationic polymerization of p-methylstyrene: initiation, chain propagation and chain termination in the presence of BF3 ∙ HF catalyst in toluene. And, in particular, the elucidation of stoichiometric composition influence of molecular system “catalyst – solvent” (BF3 ∙ HF - toluene 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, etc.) on the energy of initiation reaction of cationic polymerization for p-methylstyrene (EA is activation energy, ET is thermal effect of reaction). The calculation of initiation mechanism for stoichiometric composition 1:1, 1:2, 1:3 (catalyst:solvent) was carried out in [3-5], therefore, the purpose of this paper is to study of initiation mechanism in the presence of this catalyst by calculating the interaction reaction of monomer and initiator along the RC1-H20 coordinate in toluene with stoichiometric composition of 1:4 (within the framework of molecular model).
Methodical part
A quantum chemical study of initiation mechanism of p-methylstyrene was carried out by ab initio RHF/6-311G** method [6] in accordance with procedure, for example, described in [7–10] using software [11–13]. The reaction coordinate is RC(1)H(20).
Calculation results
The results of quantum chemical calculations (the initial model, the formed active center (AC), the energy profile of reaction, and the change in charges on the atoms directly involved in this reaction) are shown in Figs. 1-4 and in Table 1.
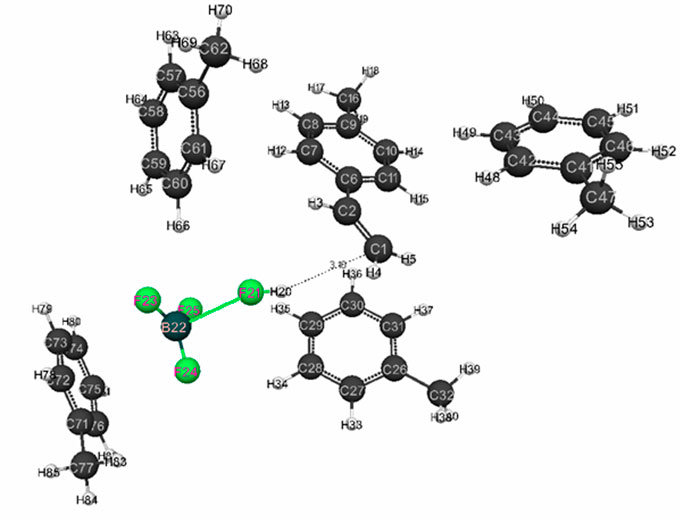
Figure 1. Initial model of interaction reaction of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene in toluene with stoichiometric composition of 1:4.
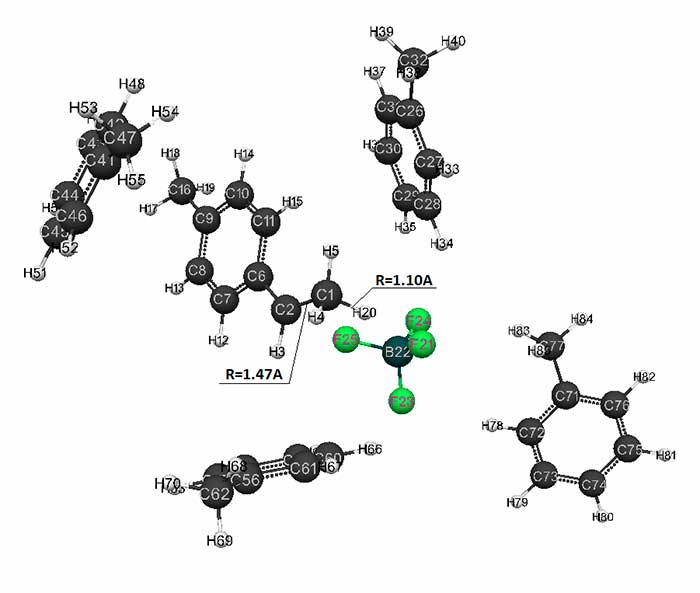
Figure 2. The result of reaction of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene in toluene with stoichiometric composition of 1:4.
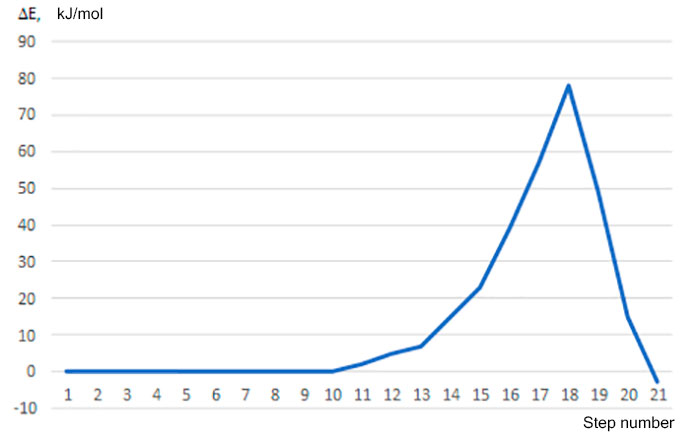
Figure 3. Change in total energy (E) along the coordinate of reaction studied (No. 1-21 is interaction steps)
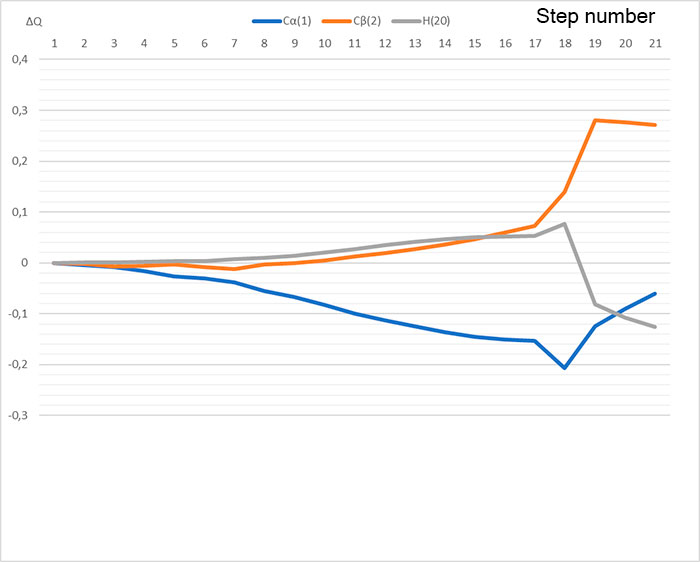
Figure 4. Changes in charges on atoms directly involved in reaction: C(1), C(2), H(20)
Table 1 shows the values of all charges on the atoms of molecular system at extremum points along the reaction coordinate RH(20)-C(1). From Table 1 it can be seen that the law of charge conservation clearly runs at each stage of components interaction.
Table 1. Charges on the atoms at extremum points (steps 1, 8, 12, 18, 21).
|
Atom |
No. of step |
|||
|
1 |
8 |
18 |
21 |
|
|
C(1) |
-0,198 |
-0,253 |
-0,405 |
-0,258 |
|
C(2) |
-0,153 |
-0,156 |
-0,014 |
0,118 |
|
H(3) |
0,116 |
0,124 |
0,159 |
0,228 |
|
H(4) |
0,114 |
0,128 |
0,152 |
0,129 |
|
H(5) |
0,111 |
0,131 |
0,163 |
0,117 |
|
C(6) |
-0,081 |
-0,086 |
-0,134 |
-0,178 |
|
C(7) |
-0,063 |
-0,054 |
-0,015 |
0,056 |
|
C(8) |
-0,100 |
-0,100 |
-0,105 |
-0,120 |
|
C(9) |
-0,118 |
-0,117 |
-0,095 |
-0,048 |
|
C(10) |
-0,097 |
-0,095 |
-0,104 |
-0,114 |
|
C(11) |
-0,066 |
-0,056 |
-0,021 |
0,055 |
|
H(12) |
0,143 |
0,143 |
0,132 |
0,135 |
|
H(13) |
0,085 |
0,085 |
0,093 |
0,109 |
|
H(14) |
0,084 |
0,086 |
0,097 |
0,110 |
|
H(15) |
0,094 |
0,098 |
0,127 |
0,154 |
|
C(16) |
-0,176 |
-0,177 |
-0,180 |
-0,188 |
|
H(17) |
0,096 |
0,095 |
0,100 |
0,114 |
|
H(18) |
0,110 |
0,108 |
0,111 |
0,118 |
|
H(19) |
0,102 |
0,107 |
0,122 |
0,143 |
|
H(20) |
0,353 |
0,363 |
0,429 |
0,227 |
|
F(21) |
-0,340 |
-0,355 |
-0,438 |
-0,446 |
|
B(22) |
0,843 |
0,842 |
0,869 |
0,886 |
|
F(23) |
-0,278 |
-0,280 |
-0,333 |
-0,406 |
|
F(24) |
-0,279 |
-0,276 |
-0,331 |
-0,403 |
|
F(25) |
-0,276 |
-0,276 |
-0,346 |
-0,471 |
|
C(26) |
-0,118 |
-0,119 |
-0,120 |
-0,121 |
|
C(27) |
-0,091 |
-0,099 |
-0,103 |
-0,127 |
|
C(28) |
-0,110 |
-0,095 |
-0,108 |
-0,112 |
|
C(29) |
-0,176 |
-0,145 |
-0,123 |
-0,129 |
|
C(30) |
-0,060 |
-0,074 |
-0,095 |
-0,085 |
|
C(31) |
-0,104 |
-0,109 |
-0,096 |
-0,114 |
|
C(32) |
-0,177 |
-0,176 |
-0,176 |
-0,173 |
|
H(33) |
0,089 |
0,086 |
0,086 |
0,085 |
|
H(34) |
0,118 |
0,114 |
0,126 |
0,151 |
|
H(35) |
0,120 |
0,114 |
0,118 |
0,139 |
|
H(36) |
0,105 |
0,098 |
0,094 |
0,091 |
|
H(37) |
0,087 |
0,085 |
0,084 |
0,080 |
|
H(38) |
0,099 |
0,097 |
0,098 |
0,092 |
|
H(39) |
0,097 |
0,098 |
0,095 |
0,090 |
|
H(40) |
0,113 |
0,112 |
0,112 |
0,115 |
|
C(41) |
-0,123 |
-0,122 |
-0,124 |
-0,126 |
|
C(42) |
-0,098 |
-0,100 |
-0,098 |
-0,096 |
|
C(43) |
-0,090 |
-0,090 |
-0,089 |
-0,085 |
|
C(44) |
-0,114 |
-0,114 |
-0,109 |
-0,107 |
|
C(45) |
-0,084 |
-0,084 |
-0,083 |
-0,086 |
|
C(46) |
-0,095 |
-0,094 |
-0,094 |
-0,093 |
|
C(47) |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,177 |
|
H(48) |
0,087 |
0,087 |
0,086 |
0,088 |
|
H(49) |
0,116 |
0,117 |
0,107 |
0,092 |
|
H(50) |
0,093 |
0,092 |
0,092 |
0,091 |
|
H(51) |
0,093 |
0,093 |
0,095 |
0,097 |
|
H(52) |
0,085 |
0,085 |
0,086 |
0,090 |
|
H(53) |
0,098 |
0,097 |
0,101 |
0,116 |
|
H(54) |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,095 |
0,099 |
|
H(55) |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,098 |
|
C(56) |
-0,114 |
-0,113 |
-0,110 |
-0,119 |
|
C(57) |
-0,100 |
-0,108 |
-0,111 |
-0,108 |
|
C(58) |
-0,082 |
-0,082 |
-0,090 |
-0,102 |
|
C(59) |
-0,127 |
-0,123 |
-0,118 |
-0,128 |
|
C(60) |
-0,087 |
-0,090 |
-0,105 |
-0,112 |
|
C(61) |
-0,113 |
-0,115 |
-0,120 |
-0,122 |
|
C(62) |
-0,175 |
-0,174 |
-0,174 |
-0,171 |
|
H(63) |
0,084 |
0,085 |
0,086 |
0,084 |
|
H(64) |
0,093 |
0,095 |
0,098 |
0,096 |
|
H(65) |
0,104 |
0,108 |
0,123 |
0,135 |
|
H(66) |
0,117 |
0,116 |
0,122 |
0,140 |
|
H(67) |
0,086 |
0,086 |
0,088 |
0,091 |
|
H(68) |
0,101 |
0,100 |
0,097 |
0,094 |
|
H(69) |
0,110 |
0,112 |
0,115 |
0,116 |
|
H(70) |
0,095 |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,092 |
|
C(71) |
-0,109 |
-0,112 |
-0,134 |
-0,154 |
|
C(72) |
-0,136 |
-0,124 |
-0,097 |
-0,096 |
|
C(73) |
-0,093 |
-0,091 |
-0,098 |
-0,100 |
|
C(74) |
-0,101 |
-0,105 |
-0,105 |
-0,107 |
|
C(75) |
-0,080 |
-0,081 |
-0,089 |
-0,091 |
|
C(76) |
-0,093 |
-0,093 |
-0,091 |
-0,090 |
|
C(77) |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,196 |
-0,184 |
|
H(78) |
0,093 |
0,091 |
0,123 |
0,143 |
|
H(79) |
0,100 |
0,099 |
0,090 |
0,088 |
|
H(80) |
0,095 |
0,094 |
0,088 |
0,083 |
|
H(81) |
0,096 |
0,095 |
0,089 |
0,083 |
|
H(82) |
0,087 |
0,087 |
0,081 |
0,076 |
|
H(83) |
0,118 |
0,119 |
0,123 |
0,131 |
|
H(84) |
0,094 |
0,094 |
0,093 |
0,074 |
|
H(85) |
0,101 |
0,099 |
0,103 |
0,111 |
Thus, in this paper we performed the quantum chemical study of initiation mechanism of cationic polymerization of п-methylstyrene under the action of complex catalyst BF3 ∙ HF in the 1: 4 ratio by ab initio method. Analysis of change in charges on atoms directly involved in this reaction (see Fig. 4), behavior of reaction fragments, breaking and formation of new bonds indicate that mechanism under study is usual acceptance of H (1)+ proton from BF3 ∙ HF catalyst and its addition to α-carbon monomer atom. The calculated values EA = 78 kJ/mol, ET = -3 kJ/mol.
References
- Kennedy, J., Cationic polymerization of olefins. Mir Publishing House, Moscow, 1978, 431 p. (in Russian)
- Odian, G., Principles of polymerization, Mir Publishing House, Moscow, 1974, 614 р. (in Russian)
- Babkin, V.А., Andreev D.S., Ignatov А.V. and others, Calculation of interaction mechanism for complex catalyst HF × BF3 with p-methylstyrene in toluene with stoichiometric composition 1:1:1 by ab initio method, Fluorine Notes, 2021, 2(135), 3-4.
- Babkin, V.А., Andreev D.S., Ignatov А.V. and others, Mechanism for initiation cation polymerization of p-methylstyrene in the presence of BF3 ∙ HF catalyst in toluene at 1: 1: 2 ratio, Fluorine Notes. 2021, 3(136), 5-6.
- Babkin, V.А., Andreev D.S., Ignatov А.V. and others, Mechanism for initiation cation polymerization of p-methylstyrene in the presence of BF3 ∙ HF catalyst in toluene at 1: 1: 2 ratio, Fluorine Notes. 2021, 5(138), 3-4.
- Cirelson V.G., Quantum Chemistry. Molecules, molecular systems and solids, Moscow, Publishing House «Binom», 2010, 496 p. (in Russian)
- V. A. Babkin and others, Quantum-chemical research of the interaction mechanism of the complex catalyst chloride aluminium-hydrochloric acid and p-methylstyrene in toluene by the ab initio method, Oxidation Communications, 2020, 43(2), 171-176.
- V. A. Babkin and others, Quantum chemical calculation of initiation mechanism of cationic polymerisation of propylene with chloride-aluminium aquacomplex, Oxidation Communications, 2020, 43(1), 24-29.
- V. A. Babkin and others, Quantum chemical investigation of the initiation mechanism of the cationic polymerisation of 4-methylpentene-1 with chloride-aluminum aquacomplex, Oxidation Communications, 2019, 42(3), 275-281.
- V. A. Babkin and others, On the mechanism of cationic polymerisation of p-isopropylstyrene in the presence of a complex catalyst boron fluoride-water, Oxidation Communications, 2019, 42(1), 56-62.
- Granovsky, A. A., Firefly version 8, 2013. http://classic.chem.msu.su/gran/firefly/index.html
- M.W. Schmidt and others, General Atomic and Molecular Electronic Structure System, J. Comput. Chem., 1993, 14, 1347-1363.
- B.M. Bode, M.S. Gordon, MacMolPlt: A Graphical User Interface for GAMESS, Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1998, 16, 133-138.
ARTICLE INFO
Received 11 November 2021
Accepted 29 November 2021
Available online June 2022
Recommended for publication by PhD Olga Bryzgalova
eLIBRARY Document Number (EDN) QRFPNY

Fluorine Notes, 2022, 142, 3-4
