Received: November 2019
DOI 10.17677/fn20714807.2020.01.01
Fluorine Notes, 2020, 128, 1-2
STUDY OF INTERACTION OF COMPLEX HF·BF3 -CATALYST WITH p-METHYLSTYRENE AB INITIO METHOD
1Babkin V.A., 1Andreev D.S., 1Ignatov A.V., 2Belousova V.S., 1Liberovskaya A.N. , 1Kozhukhova A.V., 3,4Titova E.S., 3Rakhimov A.I., 3Rakhimova N.A., 6Fomichev V.T.
1Volgograd State Technical University (Sebryakovsky br.),403343 Volgograd Region, Mikhailovka, Michurina st., 21
e-mail: babkin_v.a@mail.ru
21st Moscow State Medical University n.a. I.M. Sechenov, 119991, st. Trubetskaya, 8, bld. 2
3Volgograd State Technical University,400005 Volgograd, Lenin av., 28,
e-mail: organic@vstu.ru
4Volgograd State Medical University,400131 Fallen Wrestlers sq., 1
5Volgograd State Technical University (Architecture and Construction Institute),400005 Volgograd, Lenin ave., 28, e-mail: titova051@rambler.ru
Abstract: A quantum chemical study of cationic polymerization monomer protonation of p-methylstyrene (in the presence of complex catalyst - boron fluoride/hydrogen fluoride (HF·BF3) - with stoichiometric composition 1: 1) by ab initio method along the reaction coordinate RC1-H20 was first performed. The protonation energy barrier (79 kJ/mol) and the thermal effect of this endothermic reaction (-8 kJ/mol) were calculated. The reaction is endothermic.
Keywords: p-methylstyrene, protonation, boron fluoride/hydrogen fluoride catalyst, reaction heat, ab initio method.
Introduction
The study of elementary events behavior of cationic p-methylstyrene polymerization in the presence of complex catalyst BF3∙HF is one of the most important fundamental problems in the field polymerization for this monomer [1]. The aim of this work is to study the first stage - i.e. the initiation of p-methylstyrene in the presence of this complex catalyst by studying the interaction of monomer with initiator along the RC1-H20 coordinate in gas phase (within framework of molecular model).
Methodology
The mechanism of cationic polymerization monomer protonation of p-methylstyrene in the presence of complex HF∙BF3 catalyst was studied. The distance between the C(1) and H(20) atoms was chosen as reaction coordinate. The calculation was performed using ab initio RHF/6-311G** quantum-chemical method [2], with geometry optimization for all parameters by gradient method integrated into Firefly program [3], based on GAMESS source code [2, 4]. This method was chosen because it allows you to accurately calculate the reaction energy barriers and active centers [4]. Calculations were performed in the approximation of an isolated molecule in the gas phase within the framework of the molecular model. The mechanism of protonation of p-methylstyrene was carried out according to the method described in detail in [5] and used in [6-7]. For visual molecular representation the MacMolPlt program was used [8].
Calculation data
The change in bond lengths along the protonation path, valence angles and atomic charges of molecular system during interaction of p-methylstyrene with catalyst BF3∙HF are presented in Table 1-3.
The reaction can be divided into three stages: the first stage is the coordination stage (see steps 1–7, Fig. 3), the second stage is the stage of π-bond breaking in monomer (steps 8–17), and the third stage is the stage of formation of active center (AC) (steps 18– 21).
The atoms C(1), C(2), H(20), O(21) and B(23) are directly involved in this interaction. Let us analyze the change in charges on these atoms along the interaction path of p-methylstyrene with the BF3∙HF catalyst.
At 1st stage (steps 1–7), the atomic charge on C(1) changes from –0.202 to –0.233; at 2nd of AC formation (stage 2, steps 8–17) - from –0.246 to –0.356; at 3rd stage of final product formation (stage 3, steps 18-21) - from -0.364 to -0.221.
At 1st stage the atomic charge on C(2) changes from -0.176 to -0.178; at 2nd stage - from -0.170 to -0.055; at 3rd stage - from -0.027 to 0.114.
At 1st stage (steps 1–7) the charge on H(20) changes from 0.343 to 0.356, at 2nd stage of AC formation (stage 2, stages 8–17), from 0.361 to 0.404; at 3rd stage of final product formation (stage 3, steps 18-21) - from 0.408 to 0.206.
At 1st stage the atomic charge on F(21) changes from -0.331 to -0.349; at 2nd stage - from -0.354 to -0.431; at 3rd stage - from -0.454 to -0.468.
At 1st stage (steps 1–7) the atomic charge on B(22) remains practically unchanged (from 0.809 to 0.810); at the stage of AC formation (stage 2, steps 8–17), from 0.810 to 0.823, at 2nd stage of final product formation ( stage 3, steps 18-21) - from 0.835 to 0.848.
During of reaction, the F(21) -H(20) bonds are simultaneously broken, the C(1) -C(2) changes from double π-bond to a single σ-bond, the new bond C(1) - H(20) and the counterion [BF3∙F] is formed (Fig. 2).
The activation energy of reaction is 79 kJ/mol and thermal effect is -8 kJ/mol. The changes in atomic charges, behavior of reaction fragments, breaks and the formation of new bonds indicate that the reaction represents the usual proton acceptance from complex catalyst HF∙BF3 and protonation to the most hydrogenated carbon atom C(1).
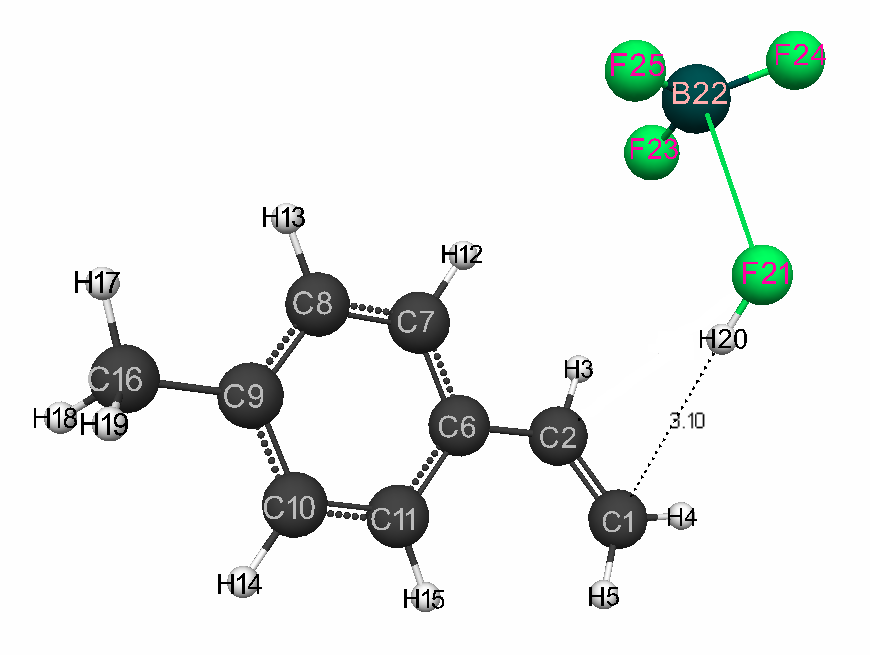
Figure 1. The structure of initial model of complex catalyst HF · BF3 with p-methylstyrene.
In Fig. 1 are presents the geometric and electronic structure of initial model of p-methylstyrene, in Fig. 2 - the its structure after interaction of catalyst with p-methylstyrene, in Fig. 3 - the energy profile of the studied reaction, and in Fig. 4 – the changes in charges of atoms directly involved in the interaction of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene.
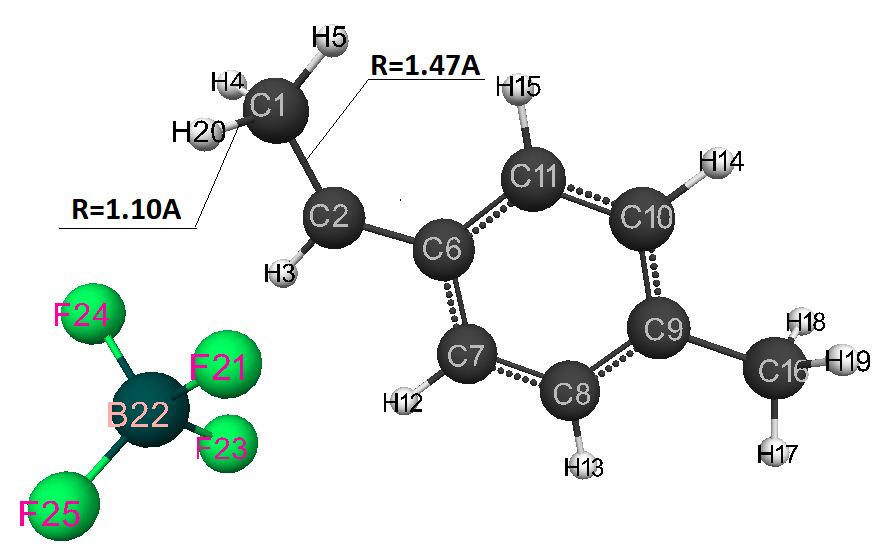
Figure 2. The final interaction structure of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene.
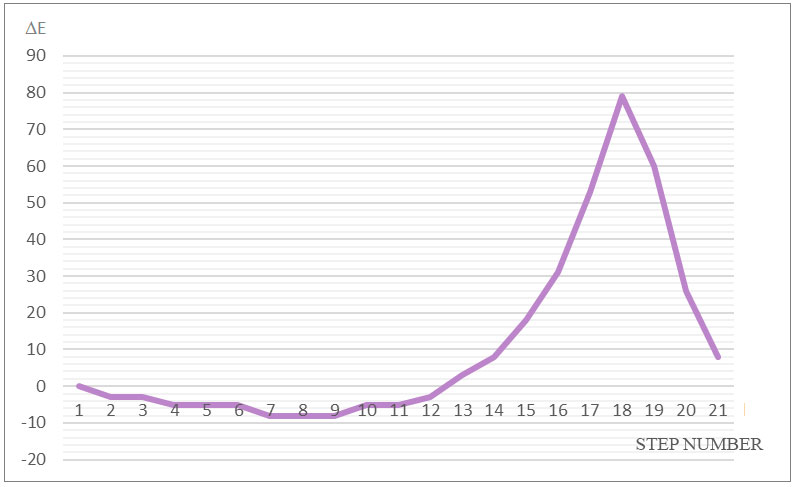
Figure 3. The total energy change (E) of studied reaction (1-21 is the steps of interaction).
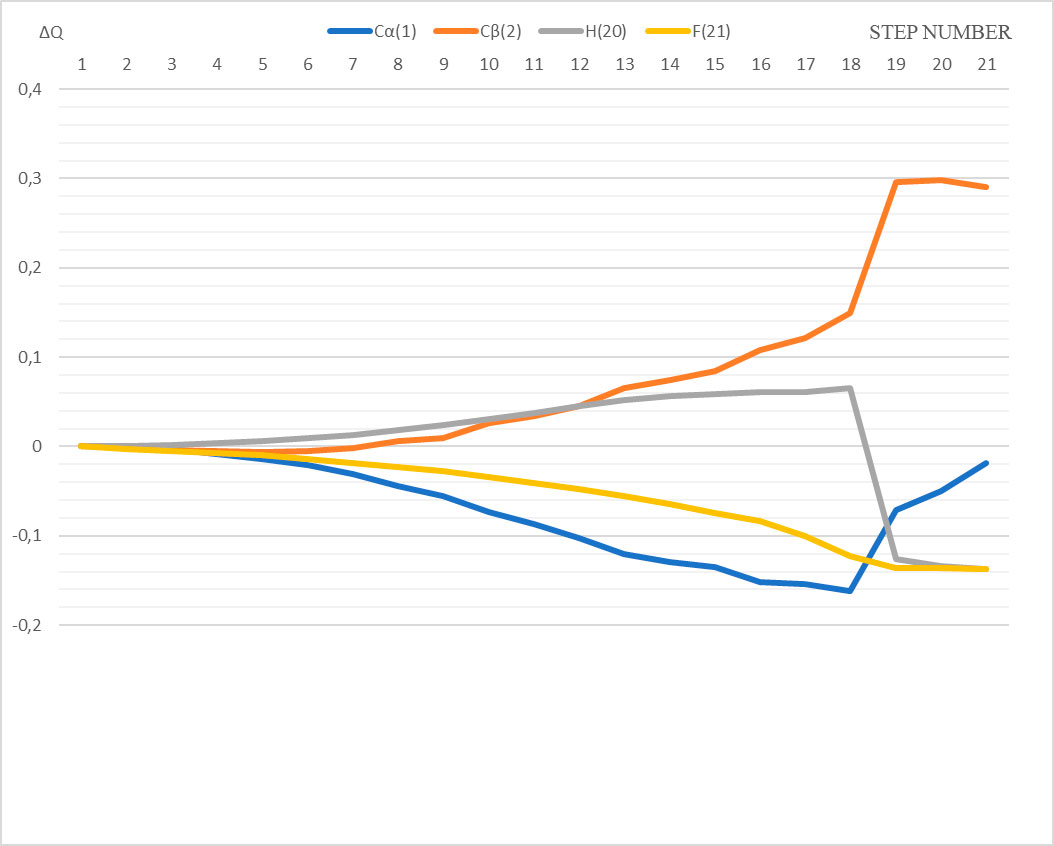
Figure 4. The change in charges on some atoms along the reaction interaction path of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene.
Table 1. The change in bond lengths along the reaction interaction path of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene
|
No of step |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
C(2)-C(1) |
1,32 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
|
H(3)-C(2) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(4)-C(1) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(5)-C(1) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
C(6)-C(11) |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
|
C(6)-C(2) |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
|
C(7)-C(6) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
|
C(8)-C(7) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
|
C(9)-C(8) |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
|
C(10)-C(9) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
|
C(11)-C(10) |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
|
H(12)-C(7) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(13)-C(8) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(14)-C(10) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(15)-C(11) |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
|
C(16)-C(9) |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
|
H(17)-C(16) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(18)-C(16) |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
|
H(19)-C(16) |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
|
H(20)-F(21) |
0,90 |
0,90 |
0,90 |
0,90 |
0,90 |
0,90 |
0,91 |
0,91 |
0,91 |
0,91 |
|
B(22)-F(21) |
2,43 |
2,42 |
2,42 |
2,42 |
2,41 |
2,41 |
2,40 |
2,39 |
2,38 |
2,37 |
|
F(23)-B(22) |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
|
F(24)-B(22) |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
|
F(25)-B(22) |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
|
H(20)-C(1) |
3,10 |
3,00 |
2,90 |
2,80 |
2,70 |
2,60 |
2,50 |
2,40 |
2,30 |
2,20 |
Continuation of Table 1.
|
No of step |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
|
C(2)-C(1) |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,33 |
1,46 |
1,47 |
1,47 |
|
H(3)-C(2) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
|
H(4)-C(1) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,09 |
|
H(5)-C(1) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
C(6)-C(11) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,42 |
1,42 |
1,42 |
|
C(6)-C(2) |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
1,47 |
1,47 |
1,47 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,39 |
|
C(7)-C(6) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
|
C(8)-C(7) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
|
C(9)-C(8) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,38 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
|
C(10)-C(9) |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,39 |
1,40 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
|
C(11)-C(10) |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,38 |
1,36 |
1,36 |
1,36 |
|
H(12)-C(7) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
|
H(13)-C(8) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
|
H(14)-C(10) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
|
H(15)-C(11) |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
1,07 |
|
C(16)-C(9) |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,51 |
1,50 |
1,50 |
1,50 |
|
H(17)-C(16) |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
1,08 |
|
H(18)-C(16) |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,08 |
1,09 |
|
H(19)-C(16) |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,09 |
1,08 |
|
H(20)-F(21) |
0,91 |
0,92 |
0,92 |
0,93 |
0,93 |
0,94 |
0,96 |
1,00 |
2,45 |
2,54 |
2,52 |
|
B(22)-F(21) |
2,35 |
2,34 |
2,32 |
2,30 |
2,27 |
2,24 |
2,18 |
1,99 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
|
F(23)-B(22) |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,31 |
1,32 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
1,41 |
|
F(24)-B(22) |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,31 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
1,40 |
|
F(25)-B(22) |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,30 |
1,31 |
1,35 |
1,35 |
1,35 |
|
H(20)-C(1) |
2,10 |
2,00 |
1,90 |
1,80 |
1,70 |
1,60 |
1,50 |
1,40 |
1,30 |
1,20 |
1,10 |
Table 2. The change in valence angles along the reaction interaction coordinate of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene.
|
No of step |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
H(3)-C(2)-C(1) |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
|
H(4)-C(1)-C(2) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
H(5)-C(1)-C(2) |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
|
C(6)-C(11)-C(10) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
C(6)-C(2)-C(1) |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
|
C(7)-C(6)-C(11) |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
|
C(8)-C(7)-C(6) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
C(9)-C(8)-C(7) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
C(10)-C(9)-C(8) |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
|
C(11)-C(10)-C(9) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
H(12)-C(7)-C(6) |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
H(13)-C(8)-C(7) |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
|
H(14)-C(10)-C(9) |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
120 |
120 |
119 |
119 |
|
H(15)-C(11)-C(10) |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
|
C(16)-C(9)-C(8) |
122 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
H(17)-C(16)-C(9) |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
|
H(18)-C(16)-C(9) |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
|
H(19)-C(16)-C(9) |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
|
H(20)-C(1)-C(2) |
66 |
67 |
67 |
68 |
69 |
71 |
72 |
74 |
75 |
77 |
|
F(23)-B(22)-F(21) |
91 |
90 |
90 |
90 |
90 |
90 |
90 |
90 |
91 |
91 |
|
F(24)-B(22)-F(21) |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
93 |
|
F(25)-B(22)-F(21) |
93 |
93 |
93 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
Continuation of Table 2.
|
No of step |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
|
H(3)-C(2)-C(1) |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
117 |
115 |
115 |
115 |
|
H(4)-C(1)-C(2) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
113 |
111 |
109 |
|
H(5)-C(1)-C(2) |
123 |
122 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
123 |
122 |
122 |
117 |
116 |
115 |
|
C(6)-C(11)-C(10) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
C(6)-C(2)-C(1) |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
127 |
128 |
128 |
129 |
|
C(7)-C(6)-C(11) |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
|
C(8)-C(7)-C(6) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
C(9)-C(8)-C(7) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
C(10)-C(9)-C(8) |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
C(11)-C(10)-C(9) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
120 |
120 |
|
H(12)-C(7)-C(6) |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
|
H(13)-C(8)-C(7) |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
H(14)-C(10)-C(9) |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
120 |
120 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
|
H(15)-C(11)-C(10) |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
119 |
120 |
120 |
120 |
|
C(16)-C(9)-C(8) |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
121 |
|
H(17)-C(16)-C(9) |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
112 |
112 |
112 |
|
H(18)-C(16)-C(9) |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
110 |
111 |
110 |
|
H(19)-C(16)-C(9) |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
110 |
109 |
110 |
|
H(20)-C(1)-C(2) |
78 |
80 |
83 |
84 |
86 |
90 |
91 |
91 |
97 |
102 |
103 |
|
F(23)-B(22)-F(21) |
91 |
91 |
91 |
92 |
92 |
92 |
93 |
96 |
107 |
107 |
107 |
|
F(24)-B(22)-F(21) |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
95 |
97 |
107 |
107 |
107 |
|
F(25)-B(22)-F(21) |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
94 |
95 |
95 |
97 |
112 |
112 |
111 |
Table 3. The change in charges along the reaction interaction path of complex catalyst HF·BF3 with p-methylstyrene.
|
Atom |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
C(1) |
-0,202 |
-0,202 |
-0,205 |
-0,210 |
-0,216 |
-0,223 |
-0,233 |
-0,246 |
-0,257 |
-0,275 |
|
C(2) |
-0,176 |
-0,177 |
-0,180 |
-0,181 |
-0,182 |
-0,181 |
-0,178 |
-0,170 |
-0,166 |
-0,150 |
|
H(3) |
0,124 |
0,125 |
0,126 |
0,127 |
0,128 |
0,129 |
0,129 |
0,128 |
0,129 |
0,125 |
|
H(4) |
0,122 |
0,123 |
0,124 |
0,126 |
0,128 |
0,129 |
0,131 |
0,133 |
0,135 |
0,138 |
|
H(5) |
0,109 |
0,109 |
0,110 |
0,111 |
0,113 |
0,114 |
0,116 |
0,118 |
0,120 |
0,123 |
|
C(6) |
-0,070 |
-0,076 |
-0,075 |
-0,073 |
-0,072 |
-0,071 |
-0,070 |
-0,070 |
-0,071 |
-0,074 |
|
C(7) |
-0,066 |
-0,061 |
-0,059 |
-0,058 |
-0,056 |
-0,054 |
-0,052 |
-0,050 |
-0,048 |
-0,046 |
|
C(8) |
-0,085 |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
-0,082 |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
|
C(9) |
-0,123 |
-0,122 |
-0,122 |
-0,122 |
-0,122 |
-0,121 |
-0,121 |
-0,121 |
-0,120 |
-0,119 |
|
C(10) |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
|
C(11) |
-0,062 |
-0,061 |
-0,061 |
-0,062 |
-0,062 |
-0,062 |
-0,062 |
-0,062 |
-0,061 |
-0,059 |
|
H(12) |
0,110 |
0,107 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,106 |
0,107 |
0,104 |
|
H(13) |
0,089 |
0,089 |
0,089 |
0,089 |
0,090 |
0,090 |
0,090 |
0,090 |
0,090 |
0,091 |
|
H(14) |
0,088 |
0,088 |
0,088 |
0,088 |
0,088 |
0,088 |
0,089 |
0,089 |
0,089 |
0,090 |
|
H(15) |
0,093 |
0,092 |
0,093 |
0,093 |
0,094 |
0,094 |
0,094 |
0,095 |
0,095 |
0,095 |
|
C(16) |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,177 |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
|
H(17) |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,097 |
0,097 |
0,097 |
0,097 |
0,097 |
0,098 |
|
H(18) |
0,109 |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,110 |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,111 |
0,112 |
|
H(19) |
0,108 |
0,107 |
0,107 |
0,107 |
0,107 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
|
H(20) |
0,343 |
0,344 |
0,345 |
0,347 |
0,349 |
0,352 |
0,356 |
0,361 |
0,367 |
0,374 |
|
F(21) |
-0,331 |
-0,334 |
-0,336 |
-0,338 |
-0,341 |
-0,345 |
-0,349 |
-0,354 |
-0,359 |
-0,365 |
|
B(22) |
0,809 |
0,806 |
0,806 |
0,807 |
0,808 |
0,809 |
0,810 |
0,810 |
0,811 |
0,809 |
|
F(23) |
-0,286 |
-0,287 |
-0,288 |
-0,288 |
-0,289 |
-0,290 |
-0,291 |
-0,292 |
-0,293 |
-0,294 |
|
F(24) |
-0,262 |
-0,264 |
-0,264 |
-0,264 |
-0,264 |
-0,264 |
-0,265 |
-0,266 |
-0,266 |
-0,268 |
|
F(25) |
-0,272 |
-0,268 |
-0,269 |
-0,269 |
-0,269 |
-0,269 |
-0,269 |
-0,269 |
-0,270 |
-0,269 |
Continuation of Table 3.
|
Atom |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
|
C(1) |
-0,289 |
-0,304 |
-0,322 |
-0,331 |
-0,337 |
-0,354 |
-0,356 |
-0,364 |
-0,273 |
-0,252 |
-0,221 |
|
C(2) |
-0,142 |
-0,131 |
-0,111 |
-0,102 |
-0,091 |
-0,068 |
-0,055 |
-0,027 |
0,120 |
0,122 |
0,114 |
|
H(3) |
0,126 |
0,127 |
0,123 |
0,124 |
0,125 |
0,124 |
0,127 |
0,134 |
0,218 |
0,216 |
0,212 |
|
H(4) |
0,139 |
0,141 |
0,143 |
0,144 |
0,145 |
0,148 |
0,149 |
0,152 |
0,164 |
0,153 |
0,139 |
|
H(5) |
0,125 |
0,128 |
0,130 |
0,132 |
0,134 |
0,134 |
0,136 |
0,140 |
0,122 |
0,112 |
0,105 |
|
C(6) |
-0,076 |
-0,080 |
-0,084 |
-0,088 |
-0,093 |
-0,097 |
-0,104 |
-0,119 |
-0,207 |
-0,210 |
-0,206 |
|
C(7) |
-0,044 |
-0,042 |
-0,039 |
-0,038 |
-0,036 |
-0,034 |
-0,030 |
-0,021 |
0,068 |
0,068 |
0,069 |
|
C(8) |
-0,083 |
-0,083 |
-0,085 |
-0,085 |
-0,085 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,088 |
-0,116 |
-0,119 |
-0,118 |
|
C(9) |
-0,119 |
-0,118 |
-0,117 |
-0,116 |
-0,115 |
-0,114 |
-0,113 |
-0,109 |
-0,055 |
-0,050 |
-0,050 |
|
C(10) |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,086 |
-0,087 |
-0,087 |
-0,088 |
-0,090 |
-0,112 |
-0,114 |
-0,115 |
|
C(11) |
-0,058 |
-0,058 |
-0,053 |
-0,053 |
-0,052 |
-0,046 |
-0,044 |
-0,037 |
0,019 |
0,023 |
0,025 |
|
H(12) |
0,104 |
0,105 |
0,102 |
0,102 |
0,103 |
0,102 |
0,103 |
0,107 |
0,185 |
0,185 |
0,183 |
|
H(13) |
0,091 |
0,091 |
0,092 |
0,092 |
0,092 |
0,093 |
0,094 |
0,096 |
0,117 |
0,118 |
0,118 |
|
H(14) |
0,090 |
0,090 |
0,090 |
0,091 |
0,091 |
0,092 |
0,093 |
0,095 |
0,110 |
0,110 |
0,110 |
|
H(15) |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,096 |
0,097 |
0,098 |
0,098 |
0,100 |
0,102 |
0,122 |
0,124 |
0,124 |
|
C(16) |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,178 |
-0,179 |
-0,179 |
-0,186 |
-0,186 |
-0,187 |
|
H(17) |
0,098 |
0,098 |
0,099 |
0,099 |
0,099 |
0,099 |
0,099 |
0,101 |
0,117 |
0,118 |
0,118 |
|
H(18) |
0,112 |
0,112 |
0,113 |
0,113 |
0,114 |
0,114 |
0,114 |
0,115 |
0,128 |
0,122 |
0,132 |
|
H(19) |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,108 |
0,109 |
0,111 |
0,112 |
0,113 |
0,132 |
0,140 |
0,128 |
|
H(20) |
0,381 |
0,388 |
0,395 |
0,399 |
0,402 |
0,404 |
0,404 |
0,408 |
0,217 |
0,209 |
0,206 |
|
F(21) |
-0,372 |
-0,379 |
-0,386 |
-0,395 |
-0,406 |
-0,415 |
-0,431 |
-0,454 |
-0,467 |
-0,467 |
-0,468 |
|
B(22) |
0,811 |
0,812 |
0,812 |
0,814 |
0,817 |
0,817 |
0,823 |
0,835 |
0,847 |
0,846 |
0,848 |
|
F(23) |
-0,295 |
-0,297 |
-0,297 |
-0,298 |
-0,301 |
-0,303 |
-0,308 |
-0,326 |
-0,453 |
-0,453 |
-0,453 |
|
F(24) |
-0,269 |
-0,270 |
-0,273 |
-0,274 |
-0,276 |
-0,279 |
-0,283 |
-0,296 |
-0,444 |
-0,444 |
-0,444 |
|
F(25) |
-0,270 |
-0,270 |
-0,270 |
-0,271 |
-0,272 |
-0,273 |
-0,276 |
-0,288 |
-0,372 |
-0,372 |
-0,371 |
References
- Kennedy, J., Cationic polymerization of olefins. “Mir” Publishing House, Moscow, 1978, 431 p. (in Russian).
- Cirelson V.G., Quantum Chemistry. Molecules, molecular systems and solids, Moscow, Publishing House «Binom», 2010, 496 p. (in Russian).
- Granovsky, A.A., Firefly version 8, 2013. http://classic.chem.msu.su/gran/firefly/index.html
- General Atomic and Molecular Electronic Structure System., M.W. Schmidt [and others], J.Comput.Chem., 1993, 14, 1347-1363.
- Potential Energy Surface of Interaction between Ethriolbicyclophosphite and Acetyl Chloride (Second Stage), V. A. Babkin [and others], Oxidation Communications. 2018, 41(2), 231-239.
- On the Mechanism of Cationic Polymerisation of P-Isopropylstyrene in the Presence of a Complex Catalyst Boron Fluoride-Water, V. A. Babkin [and others], Oxidation Communications, 2019, 42(1), 56-62.
- Quantum-chemical study of the mechanism of protonation 2,3,4,5-tetramethylstyrene by method AB INITIO, V. A. Babkin [and others], Izvestia Vstu,Volgograd, 2019, 5. 22-28 (Series: "Chemistry and Technology of Organoelement Monomers and Polymer Materials "; vol. 228, (in Russian)).
- MacMolPlt: A Graphical User Interface for GAMESS., B.M. Bode, M.S. Gordon, Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1998, 16, 133-138.
ARTICLE INFO
Received 18 November 2019
Accepted 12 February 2020
Available online February 2020
Recommended for publication by PhD. Marina Manaenkova
Fluorine Notes, 2020, 128, 1-2
