Received: March 2019
DOI 10.17677/fn20714807.2019.04.03
Fluorine Notes, 2019, 125, 5-6
QUANTUM-CHEMICAL STUDY OF THE PROTONATION MECHANISM OF p-FLUORSTYROL BY THE MNDO METHOD
V.A. Babkin1, Yu. A. Vashuta1, A.V. Kozhukhova1, D.S. Andreev1, A.V. Ignatov1, A.P. Knyazev1, A.I. Rakhimov2, E.S. Titova2,3, V.S. Belousova4, A.R. Denisyuk5, K.Yu. Prochukhan6, O.S. Rakhimova7
1Sebryakovsky branch of the Volgograd State Technical University, 403343 Volgograd Region, Mikhaylovka, Michurin Street, 21
e-mail: babkin_v.a@mail.ru
2Volgograd State Technical University, 400005 Volgograd, Lenin Avenue, 28
e-mail: organic@vstu.ru
Abstract: The mechanism of protonation of p-fluorstyrol first studied by
classical quantum-chemical method MNDO. This mechanism is a reaction of the electrophilic addition
of a proton to the double bond of a monomer. The reaction is exothermic and has no barrier character.
The gain of energy as a result of the reaction in the attack on the α-carbon atom is -540 kJ/mol.
The reaction follows the classical scheme in accordance with Markovnikov rule. Keywords: protonation mechanism, MNDO method, p-fluorostyrene, Markovnikov
rule. Study of the mechanism of protonation of p-fluorstyrol [1] is the first step in the study of
the mechanism of cationic polymerization of this monomer. Тhe aim of the present work is a quantum-chemical
study of the mechanism of protonation of p-fluorstyrol by classical semi-empirical method
MNDO. The methodology for studying the protonation mechanism of p-fluorostyrene is completely consistent
with the method used to study the mechanism for the protonation of p-ethylstyrene [2-4]. 17 Atoms
are in the system H+ ... C8H7F. M = 2S + 1 = 1 (S is the total spin
of all electrons of the system under study is equal to zero. All electrons are paired. M-multiplicity).
The total charge of the molecular system is ∑ qc = 1. The reaction coordinates were the
distances from the proton H1 to C2 (RH1C2) and from H1 to C3 (RH1C3). The equipotential surface of the interactions of
the proton with the p-fluorosterene was constructed according to the data obtained, the energy values
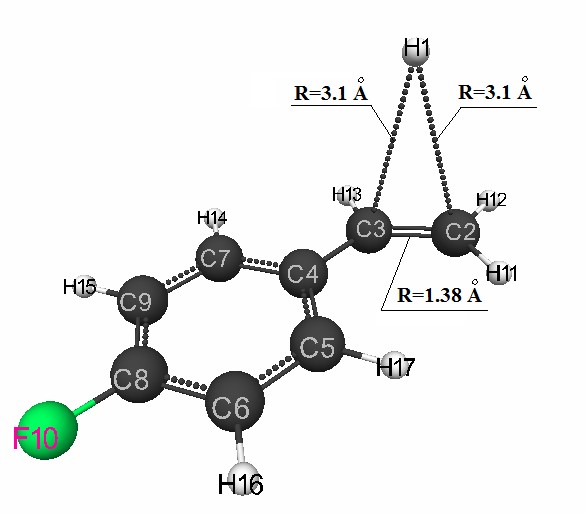
along the reaction coordinates (Fig. 4.). The initial model of the proton attack of the p-fluorostyrene
molecule is shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 1. The initial model of the attack of proton of the molecule p-fluorothyrene. For the visual presentation of molecular models was used the well-known program MacMolPlt [5].3Volgograd State Medical University, 400131 Volgograd, Pavshich bortcov Square, 1
4 I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University) ,
119991, Moscow, Trubeckaya Street, 8, building 2
5Medical College of Volgograd State Medical University, 400001 Volgograd, Kim Street, 18
6Bashkir State University, 450076, Republic of Bashkortostan, Ufa, Zaki Validi Street, 32
7Volgograd State University, 400062, Volgograd, University Avenue, 100
Methodical Part
Results and Discussion
The structure of the formed carbocation (I) after the attack of the proton H1 of the α – carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene (C2) and the rupture of the double bond of p-fluorothyrene
is shown in Fig. 2. The structure of the formed carbocation (II) after the attack of the proton H1
β – carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene (C3) and the breaking of the double
bond C2 = C3 is shown in Fig. 3. The charges on the carbocation atoms (I) and
(II) are presented in Table. 1. The change in total energy during protonation of p-fluorostyrene
is shown in Fig. 4. Negative values of the total energy of the system H+ ... C8H7F
(Е0) increases along the entire path of motion of the initiating particle H+ along the coordinates of the reaction RH1С2 and RH1С3.
The energy barrier is absent both when attacking α- and β-carbon atoms of p-fluorostyrene.
Structure (I) at 68 kJ/mol is energetically more favorable than (II). This is in full accordance
with the classical Markovnikov rule. The energy gain due to the formation of (I) is 540 kJ/mol, and
during the formation of (II) 472 kJ/mol. Analysis of the results of quantum chemical calculations, the changes of bond lengths and valence angles
along the reaction coordinate during the attack of the proton on the α- and β-carbon
atoms of a p-fluorostyrene suggests that the mechanism of protonation of the cationic polymerization
of p-fluorostyrene goes according to the classical scheme of addition of the proton to the
double bond of the monomer. Thus, we first studied the mechanism of protonation of p-fluorostyrene quantum-chemical method
MNDO. It is shown that this mechanism is a usual reaction of the proton addition to the olefin double
bond. The reaction is exothermic and barrier-free. The reactions are energetically advantageous to
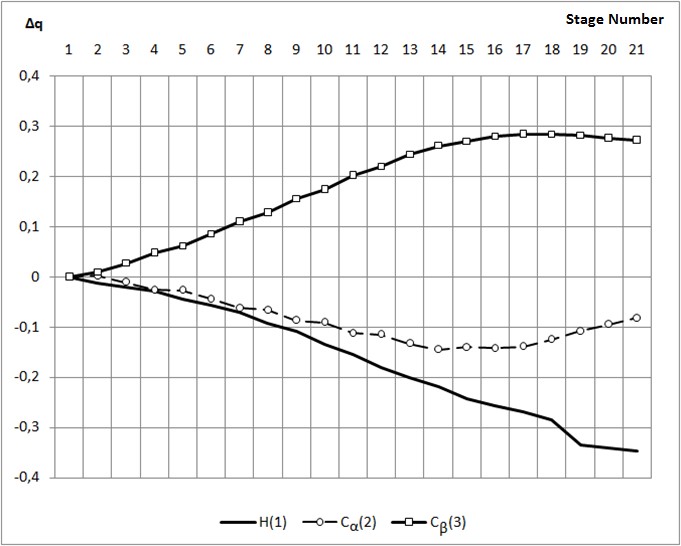
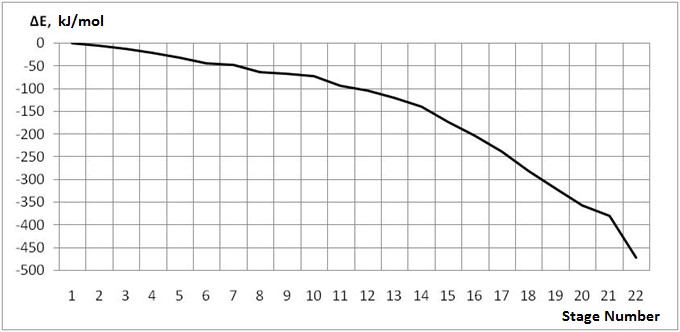
follow the classical scheme in accordance with the Markovnikov rule. Fig.2. The structure of the formed carbocation (I) after the attack of the proton H1 of the α - carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene (C2) Fig.3. - The structure of the formed carbocation (II) after the attack of the proton H1 of the β– carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene (С3) Fig. 4. Potential surface of the energy of the interactions of the proton with p-fluorostyrene. Fig. 5. The change in total energy at the accession of the proton H1 to the α–carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene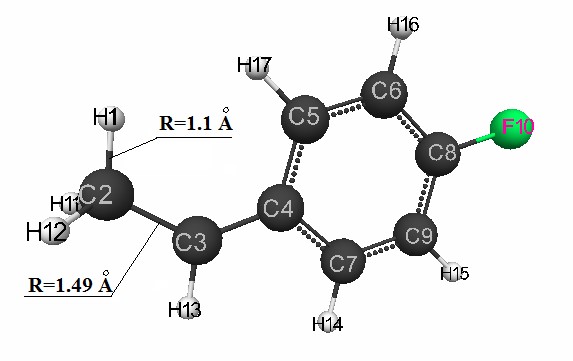
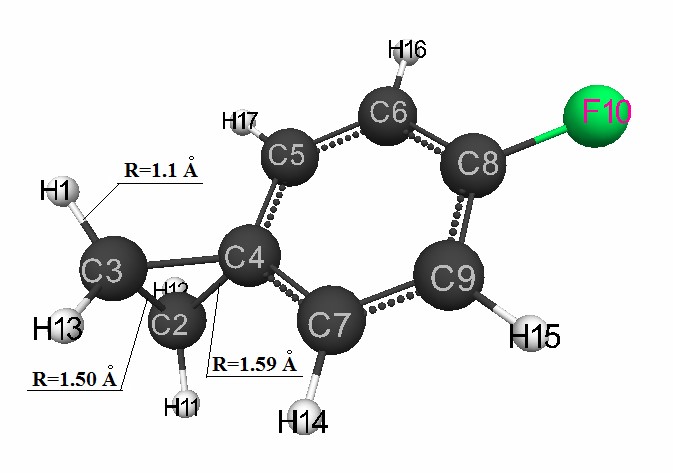
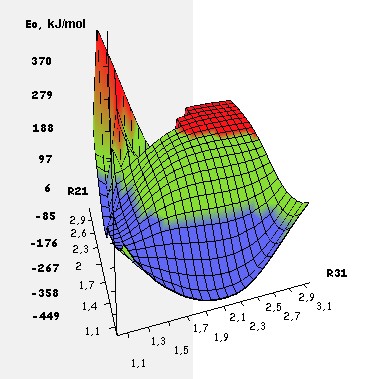
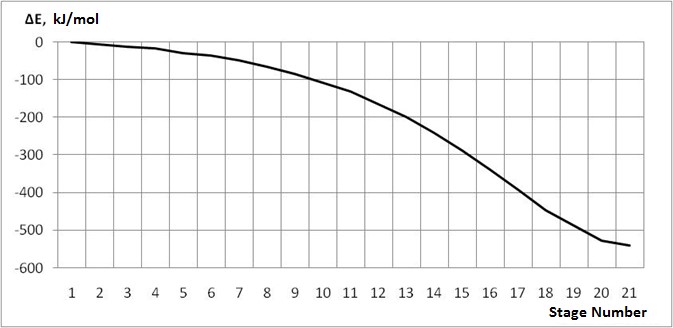
Table 1. Changes in bond lengths along the path of the H1 proton addition reaction to the α-carbon atom of a p-fluorostyrene
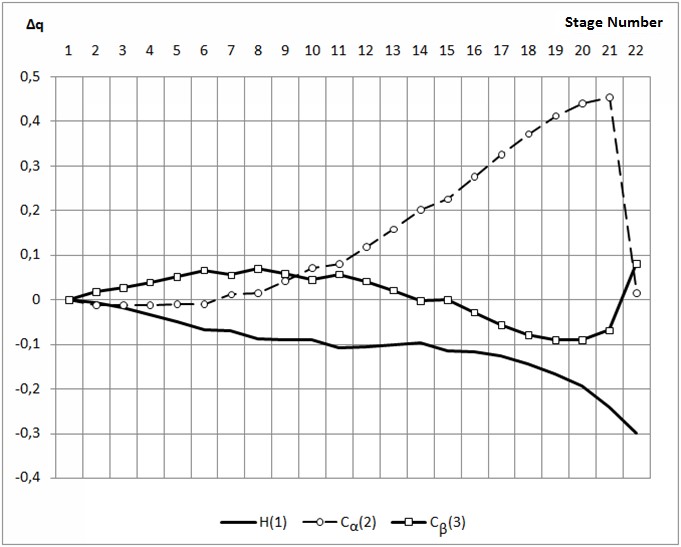
Step number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 C(2)-H(1) 3,10 3,00 2,90 2,80 2,70 2,60 2,50 2,40 2,30 2,20 C(3)-H(1) 3,10 3,00 3,00 3,00 2,90 2,90 2,90 2,80 2,80 2,70 C(3)-C(2) 1,38 1,38 1,38 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,40 1,40 1,41 1,41 C(4)-C(3) 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,42 C(5)-C(4) 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 C(6)-C(5) 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 C(7)-C(4) 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 C(8)-C(9) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 C(8)-C(6) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 C(9)-C(7) 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 F(10)-C(8) 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 H(11)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(12)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(13)-C(3) 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 H(14)-C(7) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(15)-C(9) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(16)-C(6) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(17)-C(5) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 Continuation of table 1 Step number 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 C(2)-H(1) 2,10 2,00 1,90 1,80 1,70 1,60 1,50 1,40 1,30 1,20 1,10 C(3)-H(1) 2,70 2,60 2,60 2,60 2,50 2,50 2,50 2,40 2,40 2,30 2,20 C(3)-C(2) 1,42 1,43 1,43 1,45 1,45 1,46 1,48 1,48 1,49 1,49 1,49 C(4)-C(3) 1,42 1,42 1,41 1,41 1,41 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,39 1,39 1,39 C(5)-C(4) 1,44 1,44 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 C(6)-C(5) 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 C(7)-C(4) 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,45 1,46 1,46 1,46 1,46 1,46 C(8)-C(9) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 C(8)-C(6) 1,43 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 C(9)-C(7) 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 F(10)-C(8) 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 H(11)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,11 1,11 1,11 H(12)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,10 1,10 1,11 1,11 1,11 H(13)-C(3) 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 H(14)-C(7) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(15)-C(9) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(16)-C(6) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(17)-C(5) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 Table 2. Changes in the valence angles along the reaction path for the addition of the proton H1 to the α – carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene step number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 C(3)-C(2)-H(1) 77 77 80 84 84 88 92 91 95 94 C(2)-C(3)-H(1) 77 77 72 68 68 64 60 59 55 54 C(4)-C(3)-C(2) 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 C(5)-C(4)-C(3) 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 C(6)-C(5)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 C(7)-C(4)-C(3) 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 C(8)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(8)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(9)-C(7)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 F(10)-C(8)-C(9) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(11)-C(2)-C(4) 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 98 H(12)-C(2)-C(4) 147 147 147 147 147 146 146 146 145 145 H(13)-C(3)-C(2) 116 116 115 115 115 115 115 115 115 115 H(14)-C(7)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(15)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(16)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(17)-C(5)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 Continuation of table 2 Step number 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 C(3)-C(2)-H(1) 98 97 102 106 105 109 114 113 118 117 115 C(2)-C(3)-H(1) 50 50 46 42 41 37 33 33 28 28 27 C(4)-C(3)-C(2) 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 130 130 130 C(5)-C(4)-C(3) 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 C(6)-C(5)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 C(7)-C(4)-C(3) 119 119 119 119 119 119 120 120 119 119 119 C(8)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(8)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(9)-C(7)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 F(10)-C(8)-C(9) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(11)-C(2)-C(4) 98 98 97 97 96 138 137 136 121 120 120 H(12)-C(2)-C(4) 144 143 142 140 139 95 95 95 119 120 120 H(13)-C(3)-C(2) 114 114 114 114 114 113 113 113 112 112 112 H(14)-C(7)-C(4) 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 H(15)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(16)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(17)-C(5)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 Table 3. Changes in charges along the path of the proton H1 addition reaction to the α – carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene Atom 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 H(1) 0,388 0,377 0,369 0,360 0,344 0,332 0,318 0,296 0,279 0,254 C(2) 0,059 0,061 0,048 0,033 0,032 0,015 -0,003 -0,007 -0,028 -0,032 C(3) -0,011 -0,002 0,016 0,037 0,050 0,074 0,099 0,117 0,144 0,163 C(4) -0,102 -0,111 -0,119 -0,128 -0,138 -0,148 -0,158 -0,169 -0,179 -0,190 C(5) 0,032 0,037 0,041 0,046 0,051 0,058 0,065 0,071 0,079 0,086 C(6) -0,108 -0,109 -0,112 -0,114 -0,116 -0,118 -0,122 -0,124 -0,127 -0,130 C(7) 0,048 0,051 0,056 0,062 0,066 0,072 0,078 0,083 0,090 0,096 C(8) 0,288 0,290 0,293 0,297 0,300 0,304 0,309 0,314 0,320 0,326 C(9) -0,111 -0,113 -0,114 -0,116 -0,118 -0,121 -0,123 -0,126 -0,129 -0,132 F(10) -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,123 -0,122 -0,121 -0,120 -0,118 H(11) 0,075 0,077 0,077 0,077 0,079 0,080 0,080 0,082 0,082 0,083 H(12) 0,081 0,082 0,083 0,083 0,085 0,086 0,086 0,088 0,088 0,090 H(13) 0,082 0,082 0,083 0,084 0,084 0,084 0,085 0,086 0,086 0,086 H(14) 0,089 0,089 0,089 0,089 0,089 0,090 0,090 0,090 0,091 0,092 H(15) 0,117 0,117 0,117 0,118 0,118 0,118 0,119 0,120 0,121 0,122 H(16) 0,115 0,115 0,116 0,116 0,116 0,117 0,118 0,118 0,119 0,120 H(17) 0,081 0,081 0,080 0,080 0,080 0,081 0,081 0,082 0,083 0,084 Continuation of table 3 Atom 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 H(1) 0,234 0,207 0,187 0,169 0,145 0,132 0,120 0,103 0,053 0,048 0,042 C(2) -0,053 -0,056 -0,074 -0,086 -0,081 -0,083 -0,080 -0,066 -0,049 -0,036 -0,023 C(3) 0,191 0,208 0,232 0,250 0,258 0,268 0,273 0,272 0,270 0,265 0,261 C(4) -0,199 -0,208 -0,214 -0,219 -0,224 -0,226 -0,227 -0,228 -0,226 -0,226 -0,226 C(5) 0,095 0,102 0,111 0,120 0,126 0,132 0,136 0,139 0,146 0,146 0,145 C(6) -0,134 -0,137 -0,141 -0,145 -0,148 -0,151 -0,153 -0,154 -0,158 -0,157 -0,157 C(7) 0,103 0,109 0,116 0,122 0,126 0,131 0,135 0,138 0,139 0,139 0,139 C(8) 0,334 0,341 0,350 0,359 0,366 0,373 0,379 0,383 0,388 0,388 0,388 C(9) -0,136 -0,138 -0,142 -0,146 -0,148 -0,151 -0,154 -0,155 -0,156 -0,156 -0,156 F(10) -0,116 -0,114 -0,112 -0,110 -0,108 -0,106 -0,104 -0,103 -0,101 -0,101 -0,101 H(11) 0,082 0,082 0,079 0,075 0,072 0,077 0,069 0,066 0,072 0,071 0,070 H(12) 0,090 0,091 0,089 0,085 0,083 0,067 0,062 0,060 0,073 0,071 0,070 H(13) 0,086 0,087 0,086 0,086 0,087 0,087 0,088 0,088 0,088 0,087 0,086 H(14) 0,093 0,094 0,095 0,096 0,097 0,098 0,100 0,100 0,101 0,100 0,100 H(15) 0,123 0,124 0,125 0,126 0,127 0,128 0,129 0,130 0,131 0,131 0,131 H(16) 0,121 0,122 0,124 0,125 0,126 0,128 0,129 0,129 0,130 0,130 0,130 H(17) 0,086 0,087 0,090 0,092 0,094 0,096 0,097 0,098 0,100 0,100 0,100 Fig. 6. Change of charges on some atoms when the proton H1 is attached to the α – carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene Fig. 7. The change in total energy when the proton H1 is attached to the β – carbon atom of p-fluoropyrene Table 4. Change in bond lengths when the proton H1 is attached to the β – carbon atom of p-fluoropyrene Step number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 C(2)-H(1) 3,10 3,00 2,90 2,80 2,70 2,60 2,60 2,50 2,50 2,50 2,40 C(3)-H(1) 3,10 3,10 3,00 2,90 2,80 2,70 2,60 2,50 2,40 2,30 2,20 C(2)-C(4) 2,54 2,55 2,55 2,55 2,55 2,55 2,55 2,56 2,56 2,56 2,57 C(3)-C(2) 1,38 1,38 1,38 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 C(4)-C(3) 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 C(5)-C(4) 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,43 1,43 1,43 C(6)-C(5) 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 C(7)-C(4) 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,44 1,43 C(8)-C(9) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 C(8)-C(6) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 C(9)-C(7) 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,39 1,40 1,40 F(10)-C(8) 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 1,31 H(11)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(12)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(13)-C(3) 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 H(14)-C(7) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(15)-C(9) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(16)-C(6) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(17)-C(5) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 Continuation of table 4 Step number 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 C(2)-H(1) 2,40 2,40 2,40 2,30 2,30 2,30 2,30 2,30 2,30 2,30 2,30 C(3)-H(1) 2,10 2,00 1,90 1,80 1,70 1,60 1,50 1,40 1,30 1,20 1,10 C(2)-C(4) 2,57 2,57 2,57 2,57 2,56 2,55 2,54 2,53 2,52 2,51 1,59 C(3)-C(2) 1,41 1,41 1,41 1,42 1,42 1,43 1,44 1,45 1,46 1,48 1,50 C(4)-C(3) 1,45 1,45 1,46 1,47 1,47 1,48 1,49 1,50 1,50 1,51 1,60 C(5)-C(4) 1,43 1,43 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,47 C(6)-C(5) 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,38 C(7)-C(4) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,47 C(8)-C(9) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,42 1,44 C(8)-C(6) 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,43 1,44 C(9)-C(7) 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,40 1,38 F(10)-C(8) 1,31 1,31 1,32 1,32 1,32 1,32 1,32 1,32 1,32 1,32 1,30 H(11)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,10 H(12)-C(2) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,10 H(13)-C(3) 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,10 1,11 1,11 1,11 1,12 1,13 1,10 H(14)-C(7) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(15)-C(9) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(16)-C(6) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 H(17)-C(5) 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 1,09 Table 5. Change in valence angles when the proton H1 is attached to the β – carbon atom of p-fluoropyrene Step number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 C(2)-C(3)-H(1) 77 73 72 72 71 71 74 74 77 81 80 C(3)-C(2)-H(1) 77 81 80 80 79 79 74 74 70 65 65 C(3)-C(2)-C(4) 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 C(4)-C(3)-C(2) 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 129 C(5)-C(4)-C(3) 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 124 C(6)-C(5)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 C(7)-C(4)-C(3) 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 119 C(8)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(8)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(9)-C(7)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 122 F(10)-C(8)-C(9) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(11)-C(2)-C(4) 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 H(12)-C(2)-C(4) 147 147 147 147 147 147 147 146 146 146 146 H(13)-C(3)-C(2) 116 116 115 115 115 115 115 115 115 115 115 H(14)-C(7)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(15)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(16)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(17)-C(5)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 Continuation of table 5 Step number 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 C(2)-C(3)-H(1) 84 88 92 90 94 99 103 108 113 118 124 C(3)-C(2)-H(1) 60 56 52 51 47 43 39 35 31 27 23 C(3)-C(2)-C(4) 26 27 27 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 62 C(4)-C(3)-C(2) 128 128 127 126 124 122 120 118 117 115 62 C(5)-C(4)-C(3) 124 124 123 123 123 122 122 121 121 120 118 C(6)-C(5)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 122 121 121 121 121 123 C(7)-C(4)-C(3) 119 119 119 119 119 120 120 120 120 121 118 C(8)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 C(8)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 119 120 120 C(9)-C(7)-C(4) 122 122 122 122 122 121 121 121 121 121 123 F(10)-C(8)-C(9) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(11)-C(2)-C(4) 98 98 97 97 96 95 94 92 91 91 117 H(12)-C(2)-C(4) 147 147 147 148 148 149 150 151 153 152 117 H(13)-C(3)-C(2) 115 115 115 115 115 114 113 112 109 103 119 H(14)-C(7)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 119 H(15)-C(9)-C(7) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(16)-C(6)-C(5) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 H(17)-C(5)-C(4) 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 119 Table 6. Charge change when the proton H1 is attached to the β – carbon atom of p-fluoropyrene Atom 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 H(1) 0,388 0,382 0,369 0,355 0,339 0,321 0,318 0,299 0,297 0,297 0,279 C(2) 0,059 0,047 0,048 0,048 0,049 0,050 0,071 0,075 0,101 0,130 0,140 C(3) -0,011 0,006 0,016 0,028 0,041 0,055 0,044 0,059 0,047 0,034 0,046 C(4) -0,102 -0,110 -0,119 -0,129 -0,140 -0,151 -0,154 -0,166 -0,169 -0,174 -0,186 C(5) 0,032 0,037 0,041 0,046 0,050 0,055 0,053 0,056 0,053 0,048 0,049 C(6) -0,108 -0,110 -0,112 -0,113 -0,114 -0,116 -0,114 -0,115 -0,113 -0,110 -0,110 C(7) 0,048 0,052 0,056 0,060 0,065 0,069 0,067 0,071 0,068 0,065 0,067 C(8) 0,288 0,291 0,293 0,296 0,298 0,300 0,298 0,299 0,294 0,288 0,287 C(9) -0,111 -0,113 -0,114 -0,116 -0,118 -0,119 -0,118 -0,119 -0,117 -0,115 -0,115 F(10) -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,124 -0,126 -0,128 -0,128 H(11) 0,075 0,075 0,077 0,079 0,081 0,083 0,085 0,087 0,089 0,092 0,094 H(12) 0,081 0,082 0,083 0,084 0,086 0,088 0,089 0,091 0,092 0,093 0,095 H(13) 0,082 0,082 0,083 0,084 0,084 0,085 0,086 0,087 0,088 0,089 0,091 H(14) 0,089 0,089 0,089 0,089 0,089 0,088 0,088 0,087 0,086 0,085 0,084 H(15) 0,117 0,117 0,117 0,117 0,118 0,118 0,118 0,118 0,117 0,116 0,116 H(16) 0,115 0,115 0,116 0,116 0,116 0,117 0,116 0,117 0,116 0,115 0,115 H(17) 0,081 0,081 0,080 0,080 0,080 0,080 0,079 0,079 0,077 0,075 0,074 Continuation of table 6 Atom 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 H(1) 0,281 0,286 0,292 0,272 0,271 0,261 0,243 0,221 0,194 0,147 0,088 C(2) 0,177 0,217 0,261 0,284 0,334 0,384 0,430 0,470 0,498 0,512 0,074 C(3) 0,030 0,010 -0,014 -0,011 -0,040 -0,068 -0,090 -0,102 -0,102 -0,080 0,070 C(4) -0,190 -0,195 -0,198 -0,203 -0,202 -0,201 -0,202 -0,205 -0,212 -0,215 -0,278 C(5) 0,042 0,032 0,019 0,015 0,003 -0,004 -0,006 -0,004 0,000 0,002 0,170 C(6) -0,106 -0,101 -0,095 -0,092 -0,086 -0,082 -0,081 -0,081 -0,081 -0,082 -0,176 C(7) 0,062 0,056 0,050 0,049 0,041 0,033 0,027 0,020 0,015 0,014 0,171 C(8) 0,278 0,267 0,255 0,251 0,240 0,232 0,228 0,226 0,225 0,226 0,423 C(9) -0,111 -0,106 -0,101 -0,098 -0,093 -0,088 -0,086 -0,084 -0,084 -0,084 -0,176 F(10) -0,131 -0,134 -0,137 -0,138 -0,141 -0,143 -0,144 -0,145 -0,145 -0,144 -0,093 H(11) 0,097 0,100 0,103 0,106 0,108 0,110 0,111 0,112 0,114 0,115 0,084 H(12) 0,096 0,097 0,098 0,100 0,101 0,102 0,102 0,102 0,102 0,104 0,084 H(13) 0,094 0,097 0,102 0,105 0,110 0,114 0,118 0,121 0,128 0,135 0,080 H(14) 0,083 0,081 0,080 0,079 0,078 0,076 0,075 0,073 0,071 0,070 0,106 H(15) 0,115 0,114 0,112 0,112 0,110 0,109 0,109 0,108 0,108 0,108 0,134 H(16) 0,114 0,112 0,110 0,109 0,108 0,107 0,107 0,106 0,107 0,107 0,134 H(17) 0,070 0,067 0,063 0,061 0,058 0,058 0,059 0,061 0,063 0,066 0,106 Fig. 8 - Change of charges on some atoms along the path of the addition of the proton H1 to the β – carbon atom of p-fluorostyrene
References
ARTICLE INFO Recommended for publication by Prof. S.M. Igumnov
Received 19 March 2019
Accepted 16 May 2019
Available online August 2019
Fluorine Notes, 2019, 125, 5-6
