Fluorine Notes, 2010, 70, 1-2
2,2-Bis(trifluoromethyl)propionic acid. Synthesis and propertiesA.F. Gontar, V.L. Don, E.V. Igoumnova, S.M. Igoumnov The establishment of Russian Academy of Sciences
A.N.Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds RAS Abstract. The method for obtaining 2,2-bis(trifluoromethyl)propionic acid from 2-trifluoromethyl-3,3,3-trifluoropropionic acid is proposed. The resulting substance is characterized by elemental analysis and NMR. Keywords: 2,2-bis(trifluoromethyl)propionic acid, fluoroanhydride, Yarovenko reagent. Earlier some attempts have been made to obtain 2,2-bis(trifluoromethyl)proionic acid (I) out of corresponding fluoroanhydride (II) by keeping the last one for 6 days with solution of KOH according to the scheme [I]:
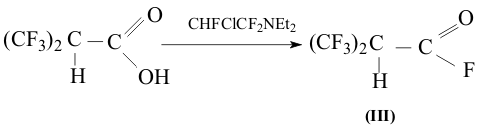
Physical characteristics of acid (I) are not listed, because, as it is mentioned in the work the formed acid is hydroscopic and it has been isolated in a form of aniline salt [1,2]. For the purpose to work up the acid (I) in its individual form and studying its properties 2-trifluoromethyl-3,3,3-trifluoropropionic acid (α- hydrohexafluoroisobutyric acid) was used for the present work. It is easily transformed into corresponding anhydride (III) with high yield by Yarovenko reagent as described in the work [3], at that it is more convenient to use the reverse mixing of reagents adding 1,1,2-trifluoro-2-chloroethyldiamine to crystal acid and trap the corresponding fluoroanhydride into the collector with potassium fluoride.
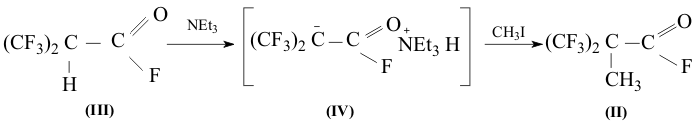
Fluoroanhydride obtained (III) was later mixed with a small excess of triethylamine while cooling and then kept in steel autoclave at room temperature. The next day methyliodide was added to the salt obtained (IV).
As a result fluoroanhydride of bis(trifluoromethyl)propionic acid (II) is formed, containing ~ 10-15% of the initial fluoroanhydride (III) b.p.=45-47oC and 31-32oC respectively. When adding fluoroanhydride (III) to aquatic solution of KOH it is easily transformed into 2,2-bis(trifluoromethyl)propioninc acid (I), which after processing of hydrochloric acid solution was extracted by methylene chloride and isolated in the individual form (b.p.=152oC ; m. p. 90-94oC no decomposition). The corresponding ethyl ester (V) was obtained using the known method out of the acid. Experimental 1.
α-Hydrohexafluoroisobutanoyl
fluoride (III). 2. 2,2-Bis(trifluoromethyl)propionyl fluoride (II).
The content of 6 experiments was then united fractioned at the rectification column. 2 fractions were obtained with b.p. = 31-32oC (II) and 45-47oC (III), with the yield of ~ 85%, the fraction (III) was used for the repeated transformation into fluoroanhydride (II) according the scheme mentioned above. 3. 2,2-bis(trifluoromethyl)propionic acid. In residue ~ 250 g of viscous masses, which were dried in vacuum over
P2O5 and afterwards distilled.
187g of crystal acid with b.p. = 152oC were obtained. Yield ~72%.
References
|
Fluorine Notes, 2010, 70, 1-2