Fluorine Notes, 2009, 64, 3-4
1,1-Dihydroperfluoroalkylamines. Report (1)
|
|
RFCH2NH2 |
BP(oC) |
Yield, % |
Yield, % |
RF CH2OH |
BP(oC) |
Yield, % |
|
HCF2 (a) CF3 (b) C2F5 (c) C3F7 (d) Cn Fg (e) |
68 38 45-50 68 87 |
55 63 60 65 65 |
96 74-75 80-81 96-97 110-110 |
32 27 27 22 18 |
||
|
C5F11 (f) C6F13 (g) C7F15 (i) C8F17 (k) |
107 +29 45/15mm Hg 56/15mm Hg |
42 38 34 32 |
55 54 50 55 |
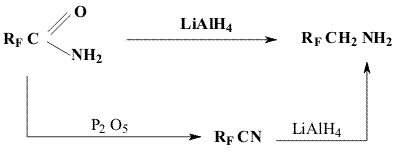
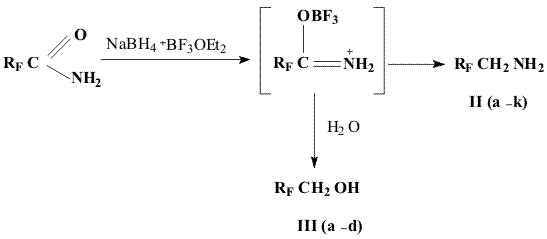
We have also found that it is more easy to obtain higher dihydrofluoroalkylamines (Rf=C5F11, C6F13, C7F15, C8F17 )by the action of NaBH4 on perfluoroalkylnitriles ( Method 2) because they are liquid products unlike lower homologues ( compare CF3CN bp=-64oC; C4F9CN bp=150oC).See also [5].
Experimental
2,2-Difluoroethylamine(IIa)
A solution of amide
of difluoroacetic acid (190 g, 2.00 mole) in 500 mL of abs. diglyme and
NaBH4 (83g, 2.19 mole) are fed in a three-neck flask ( 2 L) fitted with
a mixer, dropping funnel and a backflow condenser (the outlet is
connected with a Tischenko flask with concentrated H2SO4).
BF3*Et2O (306g, 2.16 mole) is added dropwise under stirring
resulted in heating.
After completion of addition the reaction mixture is stirred for an hour on a boiling water bath, then it is cooled with ice water and hydrochloric acid (1L) is added dropwise. The obtained mixture is evaporated to dryness on a water bath at 15 mm Hg. The strippant is collected in a cooled receiver, poured in water, the bottom layer is separated and distilled to yield 2,2-difluoroethanol (IIIa), its boiling temperature and yield are given in Table 1.
A solution of NaOH (480g, 12.0 mol) in a minimal quantity of water is added dropwise to the residue and the product with water is distilled to 100 oC. After rectification there is obtained 90 g ( 55%) of 2,2-difluoroethylamine, purity 99% (BP 68-69oC).
1,1-Dihydroperfluoroalkylamines II (b-k) and alcohols III(b-d) are obtained analogously to IIa and IIIa ( see Table 1).
1H,1H-Perfluorohexylamine (IIe), method 2
Diglyme (1.5 L) and NaBH4 (150
g. 3.95 mol) are placed and stirred in a four-neck flask (6L water
capacity) fitted with a mechanical mixer, thermometer, dropping funnel
and a backflow condenser, then perfluorohexanonitrile (570g, 1.93 mol)
is added dropwise. The reaction mixture is heated up to 60oC. After
completion of nitrile addition the reaction mass is boiled for 2 hours
and is kept overnight.
Then the reaction mass is poured cautiously in portions, as foaming occurs, into a mixture of NaOH solution ( 120g NaOH and 300 mL water) with ice (1.5 kg). The formed mass is placed in a 6L flask and distilled with steam. The lower layer of the strippant is separated to obtain 370g of the crude product that is then rectified to obtain 320 g of 1H,1H-perfluorohexylamine of 98% purity, BP 107oC in 55% yield. Amines (II b-k) are obtained in a similar way.
References
1.D.R.Husted, S.Paul, A.H.Ahlbrecht; US patent 1954 2, 691,043
2. Z.B. Papanastassion, R.I. Brini I. Org. Chem 1965, v 29, 2870-2871
3. M. Sander; Monatsheftc fur. Chtme, 95, 1964, 608-616.
4. E.R. Bissele, M. Finger, I. Am. Chem, Sos., 24, 1959, 1256-1259.
5. S. E. Ellzer, I.S. Wittman, W.I. Connick., I. Org. Chem., 30, 1965, 3645-3950
Fluorine Notes, 2009, 64, 3-4