Fluorine Notes, 2004, 37, 3-4
Perfluoropolyethers. Synthesis and Application.
Message1
B.N. Maximov, RSC Applied Chemistry
boris_maximov@mail.ru
Obtaining of Perfluoropolyethers and Their Properties
Fluorine containing polymer materials are one of the most fast developing directions of high-polymer compounds. The interest to fluoroorganic polymers can be explained by complex of unique characteristics: high thermal resistance of exclusive chemical resistance to high aggressive chemical compounds
- oxidizers etc.
Perfluoropolyethers have their special rank in the heterochain fluorine containing polymers chemistry:
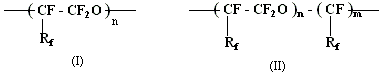
where Rf = -F, CF3
The researches, carried out in the 60-s of 20-th century in the former USSR (1,4), USA (2), Italy (3) formed the base for wide works development in this direction.
At that perfluoropolyethers of type (1) were obtained by polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene oxides. Compounds of type (2) were obtained by reaction of perfluoroolefines and oxygen in the presence of initiators (UV-radiation, fluorine etc.).
The molecular weight of polymers (1) and (2) depends on the nature of perfluoroolefine and polymerization conditions; as a rule, olygomers with relatively low polymerization grades are formed. These compounds are high-boiling liquids.
Thermal stability of polytetrafluoroethylene oxide according to data (5) is a unique one for perfluorinated polymers' temperature of max decay rate is 628 oC, while the analogous value of polytetrafluoroethylene is 568 oC.
The important feature of reactions, resulting in obtaining of polymer compounds (1) and (2), is the formation of end functional groups ( C(O)F ), that opens up wide possibilities of low molecular olygomers using for synthesis of different purposes fluorinated surfactants, and also for synthesis of new heterochain fluorine containing
polymers. (polytriazynes etc.)
There are two main obtaining methods of perfluoropolyethers.
The first way is the obtaining of perfluoroolefines with their further polymerization. In this case perfluoropolyethers of regular structure with the same ring of polymer chain are formed.
![]()
The second way is the direct liquid phase oxidization of perfluoroolefines at low temperature (-30 oC and lower). At this the products of reactions are perfluoropolyetherperoxides of irregular structure with different length of main chain rings.
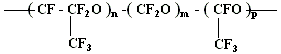
It is noticed, that low-temperature characteristics (solidification temperature, viscosity, etc.) of perfluoropolyethers of irregular structure are much better, than the ones of regular structure compounds. Owing to this circumstance the main attention in the view of practice is paid to the present perfluoropolyethers synthesis direction.
The process of obtaining of such perfluoropolyethers is carried out using mainly two methods..
1) The initiation of perfluorolefines oxidizing reaction using UV-radiation.
2) ) The initiation of perfluorolefines oxidizing reaction using chemicals, able to homolytic dissociation at low temperatures (fluorine, trifluoromethylhypofluoride etc.)
The process of perfluoropolyethers chemical synthesis is studied rather well, patented in Italy, Russia and Japan. However, a number of essential disadvantages, such as low productivity of the process, complicated technological handling, low coefficient of efficiency of UV-radiation sources ( 10% is used for efficient radiation with the length of wave 220-310 nm) and other facts limit the technological possibilities of this process.
Because of this in the last years the most attention is paid to the analysis of the synthesis process of radical co-polymerization of fluorolefines and oxygen at initiation using chemical reagents (mostly elemental fluorine), because this process is preferred by productivity and other showings. At radical co-polymerization the peroxides abundance is much lower compare to photochemical oxidization, this method has other advantages.
Fluorine Notes, 2004, 37, 3-4
