|
Synthesis and application of  -bromo-perfluoroalkylvinyl ethers -bromo-perfluoroalkylvinyl ethers
V.M.Andrushin, V.V.Drozdov
Report V. Study of physical and mechanical properties of
copolymers of fluoroolefins with  -bromoperfluoroalkylvinyl
ethers. -bromoperfluoroalkylvinyl
ethers.
1. Introduction
In report IV (1) the routes to modify fluoroplasts by copolymerization of
tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) and vinilydene fluoride (VDF) with bromo-perfluoroalkylvinyl
ethers (BrAVE) of the general formula of Br(CF2)nOCF=CF2 where n=2 ( BrAVE-2) and n=4 (BrAVE-4) have been described. The introduction
of fluoroalkylvinyl ethers to copolymerization with olefins is known to improve
processibility of the copolymers, increases their resistance to low temperatures
and their stability in aggressive chemical media.
They are used as the
second and third copolymers (2-4)
In particular, a fluoroelastomer based on triple TFE copolymer, perfluoromethylvinyl
ether and substituted perfluoroalkylvinyl ether of the general formula of
CF2=CFORfX is known.
Bromine-containing molecules
allow to synthesize new types of fluoroplasts possessing hydrophilic, conductivity,
improved solubility and better processibility. Thus, for example, the introduction
of bromotrifluoroethylene to the composition of polytetrafluoroethylene increases
amphoterism of the copolymer and reduces its melting temperature (5).
Bromine-containing monomers, for example 1-bromo-2,2-difluoroethylene, have
found wide application in processes of copolymerization with TFE, VDF, hexafluoropropylene
and other fluoroolefins to produce fluoroelastomers and general rubber goods
based on rubbers (6-9). In this case bromine atoms are convenient active
centers to form space-network structures (10-16). There are known many polymer
compositions of radical solidification based on bromated and iodinated fluoroelastomers
(17-21).
It was planned to produce new fluoroplasts and fluoroelastomers
with a set of performance characteristics peculiar to copolymers based both
on perfluoroalkylvinyl ethers and on bromine-containing fluoromonomers using
BrAVE monomers as modifiers of fluoropolymers in reactions of copolymerization
with fluoroolefins.
In the present paper we state the results of the
determination of general physical and mechanical characteristics of copolymers
of BrAVE with the most widespread fluoromonomers, TFE and VDF, and their
resistance in different aggressive chemical media.
2.Test procedure
Physical and mechanical characteristics of materials were determined on the basis
of the results of tensile tests carried out on a test machine of 2055 P-05
type of "TochPribor" (c. Ivanovo, Russia) made.
Test samples were two-sided
scoops manufactured by blanking from films with a special knife. The machine
is equipped with a hermetic autoclave of a special design with controllable
electrical heating to provide testing the samples in different aggressive
chemical media.
Based on the tensile test results the following physical
and mechanical characteristics were calculated:
- breaking stress, MPa
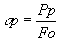 ,
MPa ,
MPa
where Pp is the load at the sample destruction, N
Fo is
the starting surface of the sample cross-section, cm;
- modulus of elasticity, MPa
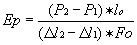 ,
MPa ,
MPa
where P1,P2 are the loads chosen at
the initial linear part of the tensile diagram, N;
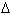 l1, l1,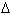 l2 - are the sample elongation at the loads of P1,P2 respectively,
cm; l2 - are the sample elongation at the loads of P1,P2 respectively,
cm;
lo- is the length of the sample test part, cm;
- percent elongation
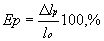
where 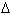 lp is the sample elongation at rupture, cm; lp is the sample elongation at rupture, cm;
- percentage change of the breaking stress
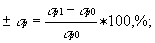
where 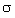 p1 is the breaking stress in a medium, MPa; p1 is the breaking stress in a medium, MPa;
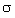 p2
is the breaking stress in air, MPa; p2
is the breaking stress in air, MPa;
- percentage of the modulus of elasticity
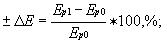
where Ep1 is the modulus of elasticity in a medium, MPa;
Epo is the modulus of elasticity in air, MPa
- change of percent elongation
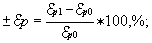
where 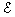 p1 is
the percent elongation in a medium, %; p1 is
the percent elongation in a medium, %;
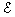 po is the percent elongation in air,%. po is the percent elongation in air,%.
To determine chemical
resistance of the copolymers, samples were subjected to aging for 7 days in 20% solutions of sulfuric
acid and caustic soda at a temperature of 90oC and then their physical and mechanical
properties were determined at tensile at 20oC.
2. Study of physical and mechanical characteristics of copolymers
of TFE.
The fluoroplast of F-10 type widely used for making flexible pipelines, gasket materials etc. was used
as the comparison standard.
The comparison of modificating affect of BrAVE monomer and other
fluoromonomers such as 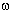 -fluorosulfuryl-perfluoroalkylvinyl ether (FS-141), perfluoroallylvinyl ether , perfluoroallylalkylvinyl
diether was of an undoubted interest also. Some results of the conducted experiments are given in
Table1. -fluorosulfuryl-perfluoroalkylvinyl ether (FS-141), perfluoroallylvinyl ether , perfluoroallylalkylvinyl
diether was of an undoubted interest also. Some results of the conducted experiments are given in
Table1.
The study has shown that the strength characteristics and modulus of elasticity considerably
increase after treatment in alkali for almost all types of copolymers of TFE tested. Some reduction
in the modulus of elasticity of copolymers with FS-141 was observed in tests in sulfuric acid against
a background of some increase in the strength parameters. Deformation characteristics of the all
copolymers of FS-141 tested ( with different content of comonomer) are reduced in aggressive media
and to a greater degree in aging in alkali.
As regards to BrAVE monomers, all their physical
and mechanical parameters increase both in acid and in alkali media and the modulus of elasticity
and breaking stress increase to the greatest extent.
It is seen from Table 1 that effectiveness
of BrAVE monomers goes down with the chain length growth. The increase in the strength characteristics
of copolymers based on BrAVE after their aging both in acid and in alkali is explained by additional
cross-linking of the copolymer which takes place at the contact of the bromine-containing copolymer
with an aggressive medium.
|
