Fluorine Notes, 1999, 7, 9-10
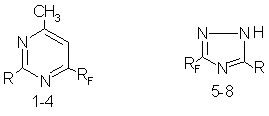
Main directions of fragmentation of molecular ions of perfluorosubstituted 1,3-diazines and 1,2,4-triazoles.L.M.Popova, S.V.Vershilov Investigation of mass-spectra of heteroaromatic compounds has shown that pyrimidines, 1,2,4-triazoles and most of their haloido-, alkyl- and amino- derivatives as conjugated systems possess quite a high (Wm over 10%) stability with regard to electron impact [1-3] , which allows to accurately determine the molecular mass of the compounds. Thus, the relative intensity of molecular ion M+ of unsubstituted pyrimidine is 42% and at its dissociation two molecules of hydrogen cyanide are split off consequently resulting in formation of fission ions [C3H3N]+ and [C2H2]+ with the intensity of 15 and 16% respectively. [4]. The mass spectrum of 1H-1,2,4-triazole is similar to that of 1,2,3-triazole. On the basis of data on mass-spectra of deutero analogues of 1,2,4-triazole and some its derivatives it has been concluded[4] that in gas phase M+ of these compounds exists in two asymmetric tautomeric forms. Decomposition of derivatives of 1,2,4-triazole runs mainly by elimination of HCN or RCN according to different mechanisms [4], elimination of the molecule N2[2] is slight ( peak intensity is less then 1%) in the presence of perfluorosubstitutes in the azole molecule. The technique of chromato-mass-spectroscopy ( electron impact, 70eV) was used for confirmation of the structure and composition of 6-perfluorosubstituted 2-amino- (1), 2-hydroxy- (2), 2-mercapto- (3) and 2-methylthio- (4) 4-methylpyrimidines and 3-perfluorosubstituted 5-amino (5-7) and 5-mercapto- (8) 1,2,4-triazoles.
RF = C6F13 R = NH2 (5), SH (8), SCH3 (4); CF(CF3)OC3F7 R = NH2 (1, 6), OH (2), SH (3); CF(CF3)OCF2CF(CF3)OC3F7 R = NH2 (7). In the mass-spectra of the substances investigated, the peaks of molecular ions [M+] , typical for halogen-containing heterocyclic compounds [3], are present along with peaks of isotope ions [M+1]+ , as well as [M+2]+ ( less 1then %) in spectra of 2-mercapto- (3), 2-methylthio- (4) 4-methylpyrimidine and 5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (8). A high intensity of the peaks of molecular ions (39-78%) is an evidence of considerable resistance of 3-perfluorosubstituted triazoles to electron impact. The analysis of the mass-spectra (Table ) allows to assume that primary fragmentation of molecular ions takes place mainly as a result of simple break as well as benzyl one of perfluorosubstituent of the side chain. The peaks of ions [M-F]+ are present in the spectra of investigated pyrimidines (1-4) and 1,2,4-triazoles. The ions [M-CF3]+, [M-C2F5]+ [M -C3F7-O]+ are typical for fragmentation of compounds containing perfluorinated substituents as well as the presence of peaks of ions with m/z 31 [CF]+ , 69 [CF3] +, 76 [C2NF2]+, 77 [HC2NF2]]+, 78 [H2C2NF2]+, 100 [C2F4]+, 119 [C2F5]+ and 169 [C3F7]+ in the spectra of compounds (1-4)[3]. The fragments with m/z 164 and 133 (5), 183 and 133 (6,7) and 150 (80 are of great interest, they obviously are formed as a result of perfluorosubstituent decomposition. The intensive peaks of fragments with m/z 183 ( to which a gross-formula C 2F 4C 2N 4H 3 may be assigned) in the spectra of 5-amino-1,2,4-triazoles is bound up with break of the ether bond C-O in the perfluorinated substituent, elimination of high stable difluorocarbene followed by skeleton rearrangement [3]. But in contrast to perfluoroalkanes [3], the peaks of [M-F] + ions are not the maximal. The peaks of fission ions with m/z 51,44,29,28 and some others are typical for fragmentation of pyrimidine derivatives [6,7]. The peaks with m/z 45 (CHS) [7,8] are typical for mass-spectra of S-containing compounds(3,4). The presence of peaks of characteristic ions with m/z 150 in the spectrum of 5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (8) and with m/z 164 and 133 (5) , 183 and 133 (6,7) in the spectra of 5-amino-1,2,4-triazoles as well as peaks of ions with m/z 57, 42,41,28, 27 is typical for fragmentation of triazole derivatives [9-11]. This allows to use this method for identification of such compounds. Thus, we have analyzed the mass-spectra of some 6-perfluorosubstituted 1,3-diazines (1-4) and 3-perfluorosubstituted 1,2,4-triazoles (5-8), determined the molecular masses of the compounds, determined the main regularities of fragmentation of molecular ions under electron impact. Table Mass spectra of 6-fluorosubstituted 4-methylpyrimidines (1-40 and 3-perfluorosubstituted 5-amino- (4-7) and 5-mercapto- (8) 1,2,4-triazoles (EI, 70eV)
References
|
Fluorine Notes, 1999, 7, 9-10