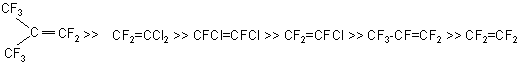Fluorine Notes, 1999, 6, 9-10
Synthesis of fluorinated ethers from fluoroolefins and polyhydric alcohols.V.M Andriushin, V.V.Kirillov Introduction Methods to produce monoethers from monohydric aliphatic, aromatic alcohols and phenols are well known. One of them is nucleophilic addition of fluoroolefins to alcohols. This reaction was used in development of inhalation anesthesia remedies. According to the results of investigations of interactions of fluoroolefins and aliphatic alcohols (C1-C3) , the following activity series can be derived:
For example, the two first members of this series react at cold with methanol, the simplest alcohol, while the last member, tetrafluoroethylene, does not form ethers even at heating and elevated pressure. At these conditions a telomerization reaction to form fluorinated telomer-alcohols of the following formula: H(CF2CF2)nCH2OH, where n=1-7 is passed intensively. It is also known from literature data that the reaction of addition of fluoroolefins to alcohols is passed more smoothly in the presence of solvent and over catalyst. As regards polyhydric alcohols, the available scanty information allows only to conclude that the reactivity of olefins is significantly lower. This paper presents the results of investigations of interactions of olefin halides with polyhydric alcohols (part1) and subsequent fluorination of the ethers obtained (part 2). Part 1. Study of interactions of olefin halides with polyhydric alcohols The reaction of olefin halides with polyhydric alcohols is of great practical interest as one of the stages of development of new polyfunctional derivatives of perfluorooxacarbonic acids by means of producing the appropriate ethers, their fluorination, formation of the end carboxyl groups and their conversion to necessary functional derivatives. To study this reaction, interactions of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), hexafluoropropylene (HFP) and trifluorochloroethylene (TFCE) with ethylene glycol (EG), glycerin (GL), pentaerythrite (PE) and diethylene glycol were investigated. We obtained similar structures of ether type by interaction of perfluoroisobutylene (PFI) with telomeric alcohols. The effect of the following main reaction conditions on the synthesis results was studied: temperature (50-1000C), alkali concentration (15-25 % of the alcohol amount), the presence of solvent (diglyme) and catalyst (triethylbenzylammonium chloride). It was found that depending on the synthesis conditions, products both of complete and of partial addition of fluoroolefins to hydroxyl groups may be formed, and the reaction takes place more completely and smoothly in the presence of a solvent. Diglyme was found the most effective among solvents, apparently due to its specific ability to polarize molecules of fluoroolefins. In case of TFE, the reaction takes place only in the presence of a solvent and catalyst (triethylbenzylammonium chloride). It was found experimentally that the conditions of synthesis of ethers from fluoroolefins and from polyhydric alcohols are close enough with the exception of the contact time:
Some results at the temperature of 700C and the ratio of alcohol:diglyme = 1:20 are given in the table.
Dyglyme was distilled and carefully dried before use. TFE was carefully purified from stabilizers. Other fluoroolefins were used after drying with magnesium sulfate. The reaction mass had yellow-orange color. It was washed with water to separate the goal compounds, the water-ether mixture was stratified and the produced ether was separated and dried. The purity of the goal products was 96-98% according to GLC data. Similar results were obtained in the reactions with PFI, and the reaction rate was twice as much than that for TFCE. The results obtained confirm the activity series given for monohydric alcohols: 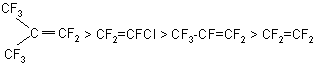
In the absence of solvent the reactions with TFE can be carried out only in the presence of sodium alcoholate, especially since it rapidly loses its activity. We failed to isolate the ether layer during water washing because strong evolution of heat and evolution of gaseous products of destruction took place. In the reactions with HFP, the ether yield attained 45% and the purity was about 70%. As regards the interaction of TFCE and PFI, the reaction is passed vigorously enough both in the presence of catalyst and in its absence. This phenomenon is of particular practical interest because the ethers based on TFCE and other chloroolefins are most suitable for synthesis of various polyfunctional derivatives. Identification of the reaction products was carried out by F NMR, IR-spectroscopy and GL chromatography methods. The obtained results allow to establish production of laboratory samples and pilot batches of di- ,tri- and tetraethers based on fluoroolefins. |
Fluorine Notes, 1999, 6, 9-10